General Tips
- Upgrade from older SMC modems. Newer Cisco or Netgear modems have better electronics and thus allows for higher speeds.
- If sharing the Comcast with a VoIP application, choose at least one up from the base package.
- Reboot your modem once a month. Comcast advises frequent modem reboots to improve performance. If you must reboot more than once/month, ask for a new modem.
- Go to firewall settings and disable "Gateway Smart Packet Detection".
Your Building Coax Cabling Must be Perfect
- The cable modem must be installed next to your router in your computer area/room and on a UPS.
- The cable drop from the mainline to your modem must be RG11 cable.
- Remove old HBO filters from the tap plate used in the days of an analog cable TV.
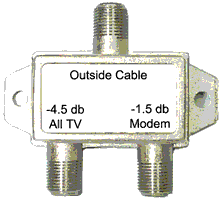
- Replace the "even" splitter between outside cable and cable modem with a quality "uneven" two-way splitter (as pictured). The -1.5 goes to the cable modem.
- We discourage sharing of Internet cable with TV or cable dial tone boxes as this is a point for noise ingress and power loss.
- Check to see if a temp mainline splitter was installed when your neighbor got Comcast and the installer split the last available port of your mainline tap and cut your signal in half.
Verify Signal Quality Levels
Inbound noise to the cable plant from the premise is the #1 issue affecting Comcast service.
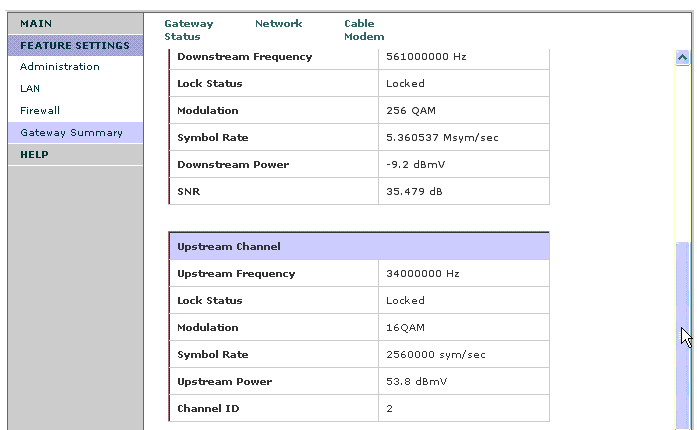
This issue results in a poor upstream signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio. Endusers can't measure upstream SNR from the premise but you can extrapolate it by the upstream power the Comcast CMTS (head-end) commands the modem to transmit to push the signal trough the high noise level back to Comcast.
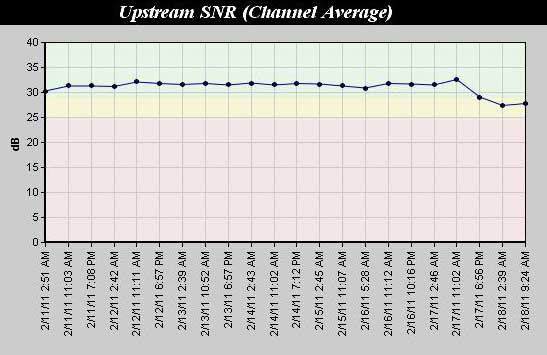
Comcast service delivery is like municipal water service delivery. It's a system of interconnected large and small diameter pipes. Comcast states that a working "water pressure" range is -15db to +15db with lower than -11db as being in the "yellow range". Unofficially, Comcast insiders state it should be at 0db for best performance. The picture below shows a Comcast cable modem diagnostic page with acceptable upstream (SNR) signal to noise ratio.
Good SNR is especially important if the downstream power cannot be improved. Inside premise cabling defects such as a loose connection to a TV can cause poor upstream SNR. On critical or new cable modem installs, we will discourage connection of cable TV or Arris box POTS lines until performance is proven. It is the customer's responsibility to correct any deficiencies on interior cabling.
| Item | Minimum specs | Best we have seen |
|---|---|---|
| Down Power in | >= 0 db | 0 db |
| Down Signal-to-noise (SNR) | > 32 db | > 37 db |
| Up Power | < 42 db | < 35.5 |
Your cable company will verify poor signal levels with a system called scout.
| CM-00:22:2d:71:ba:a4 | |
| IP Address of Modem | 73.141.177.67 |
| Current CMTS Status | ACTIVE |
| Current Firmware | 1.4.0.49.2-CCR |
| Device Make/Model | SMC Networks SMCD3G-CCR |
| Device Up Time | 104 days 9:14:35.05 |
| Docsis Capability | DOCSIS 3.0 |
| Downstream Signal Quality (SNR) | 35.0 |
| Modem Lost Syncs | 1 |
| Modem Resets | 5 |
| Receive Power Level (downstream) | 0.1 Dbmv |
| Receive Power Level (upstream) | 2.8 Dbmv |
| Serial Number of the Device | H29421C3C4 |
| Transmit Power Level (upstream) | 48.0 Dbmv |
| Upstream Signal Quality (SNR) | 32.0 |
| Current Device Status | 6(Online) |
| End of Life Status | No |
| Modem Boot File | d11_m_smcd3gccr_bcistarter_c05.cm |
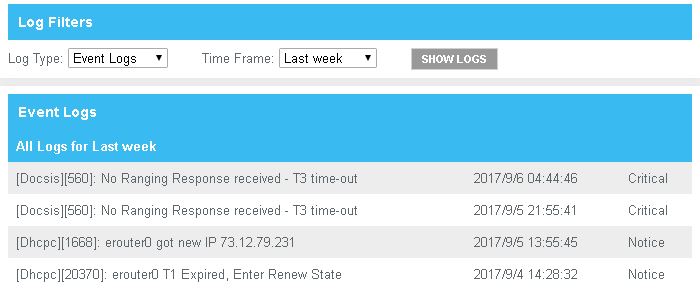
Check your Event Logs
| T | Timeout Description // Symptoms | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | RARE OCCURANCE: Modem has not received any periodic Upstream Channel Descriptor messages from the CMTS within the timeout period. // Modem will not range upstream and thus will never go online. | Cable tech must inspect the outside plant and also compel the headend office to fix the downstream signal. |
| T2 | RARE OCCURANCE: The cable modem did not receive a broadcast maintenance opportunity in which to transmit a RANGING REQUESTS within the T2 timeout period of @ 10 seconds. The cable modem is resetting its cable interface and restarting the registration process. // Modem will not range upstream and thus will never go online. | Cable tech must inspect the outside plant and also compel the headend office to fix the downstream signal. |
| T3 | COMMON OCCURANCE: The cable modem has sent 16
RANGING REQUESTS without receiving a response from the CMTS
within 200ms. 200ms delay in a VoIP packet would result in poor
audio! T3 error is caused by noise on the
upstream channel. These errors go hand-in-hand with your cable
modem set by the CMTS to crank up it's upstream power level to
punch through the noise. // Occasonal disconnections.
A few of these errors daily is ok. Several per hour is an issue consecutive errors is a serious issue aka an area outage. |
Replace bad cables and tighten loose connectors.
Recable with RJ-11 Quad shield cable. Remove extra splitters. Tell your neighbors to also clean up their cabling! If you are a business next to residential rental property, that is going to be an issue. Call for a technician visit to inspect and fix cables outside |
| T4 | COMMON OCCURANCE: SService outages or maintenance activity, impairment in the downstream, major faults like damaged drops, or mainline suckouts.T4 timeouts can become commonplace when node capacity approaches 90% due to TDMA(Time Domain Multiple Access) transmit opportunities simply being unavailable.// Will cause a disconnect with each occurance. | Same as above. |
| T6 | RARE OCCURANCE: DOCSIS configuration file is corrupt, reload // modem will not come online | Call Comcast support and ask them to re-provision the modem. |

Secure RF Caps for Unused Taps
Pictured above is a four position mainline tap with one unused position properly capped to prevent RF intrusion.
Orange RG-6 direct burial cable must be used for below ground installs. The cable may turn yellow with age and exposure to the sun's UV rays. Check the cable for cuts to the plastic sheath.
Ground the Cable per NEC Code Section 800-33
Pictured is a Comcast cable that has NOT been grounded. The red arrows indicates where a #14 or better ground wire should run to the building ground or at least to a ground rod.
Per National Electrical Code section 800-33. Cable grounding.
The metallic sheath of communications cables entering buildings shall be grounded as close as practicable to the point of entrance or shall be interrupted as close to the point of entrance as practicable by an insulating joint or equivalent device.
The grounding conductor shall not be smaller than No. 14.
The grounding conductor shall be run to the grounding electrode in as straight a line as practicable.
Bonding of Electrodes. A bonding jumper not smaller than No. 6 copper or equivalent shall be connected between the communications grounding electrode and power grounding electrode system at the building or structure served where separate electrodes are used. Bonding together of all separate electrodes shall be permitted.
